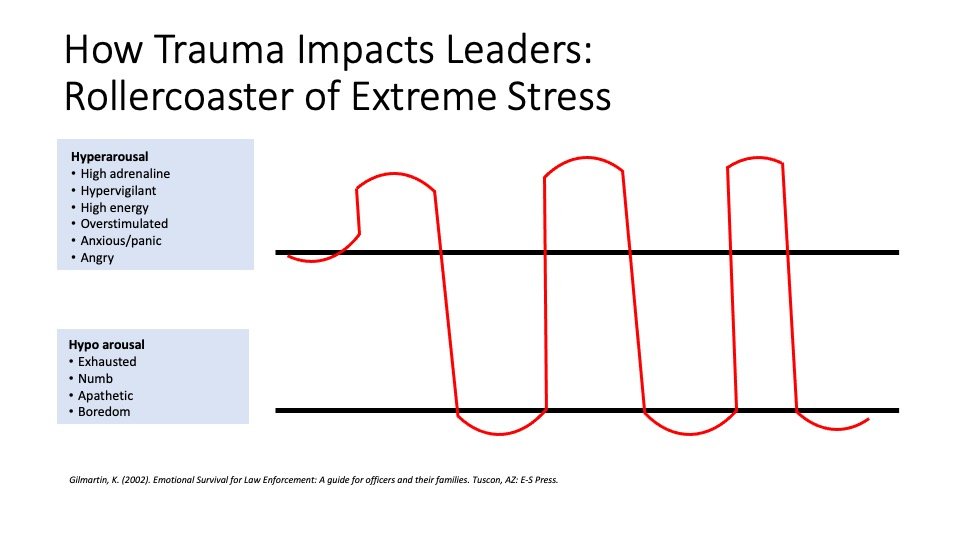
When you are on-shift, you are on the top of this illustration—you are hit with a flood of adrenaline— you are in a necessary state of hypervigilance—paying attention, highly energized, ready for action. And when you go off shift you are below the lines-- your body sinks into a state that may be exhausted, apathetic, and irritable.[v] As Gilmartin, who works with police professionals states, “for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction,” and this rollercoaster is your body’s attempt to recover from the onslaught of stress hormones. This recovery typically takes 18-24 hours making it likely that on most days you will barely get the time to recover before you are back in it. You may notice that you feel more ‘alive’ at work. That you feel more like ‘yourself’ with the adrenaline and you feel more detached or numb when you are home. This crash in to numb may make it harder to connect to your families or friends when you are home, or make it harder to connect with them via phone or FaceTime if you have moved away to protect them. Trauma makes it seem like the only people we can connect with are people who are in the trauma with us. It’s a ‘war buddy’ phenomenon: the people we are with ‘above the line’ can feel more connected to us than the people we are with ‘below the line.’ This doesn’t mean we love them less, but this is physiological and psychological response to trauma. But it doesn’t have to rule your reality, and there are ways to manage this roller coaster and bring awareness to your recovery and reconnection to support survival in this difficult time.
What can health professionals do right now to support recovery and repair of the physiological and psychological trauma of Covid-19.
1) You have to own the roller coaster. By being aware of the impact on your body and brain you have some choices about what actions you can take to bring yourself into the best possible state.
2) Plan your transitions between work and home: create a ritual that helps you connect with people, and previous aspects of yourself (favorite music, something nourishing).
3) Avoid television, or things that make you more likely to sit in ‘numb’ for too long.
4) Attend to your body. Above the line, you want to do things that ‘soothe’ you. Below the line you want to do things that bring you back into a feeling state.
5) Start wherever you are: sometime simply stating how you feel “I feel numb” allows you to be heard and understood and help you feel more connected to yourself and others and mitigate the experience of feeling detached.
What can loved ones do right now to support recovery and repair of their health care professional’s physiological and psychological trauma of Covid-19:
1) Stay engaged: Imagine holding the other end of the rope. Sometimes you will hold it lightly, and sometimes you will tug on it. But stay connected in ways that you can.
2) You need to have conversations—even when they feel awkward and repetitive—for all of you during this time: what is helpful, what is stressful, what are your signs of stress, how will I know you need help, what are you grateful for, what brings you joy?
3) Your health professional may not be able to support you in the way you need right now, who else can be on your team to support you and your family right now? Who else can you talk to to make sure you aren’t alone with your worries either?
4) Reacquaint yourselves to the activities that brought you joy, and try to some new things as well. Be curious about what is important to you now.
What can healthcare leaders do right now to support repair and recovery of their colleagues and healthcare professional’s physiological and psychological trauma of Covid-19.
1) Help your health professionals and colleagues understand and own the impact of stress and trauma. Normalize it and encourage conversation and coping.
Make sure that the mental health resources are easily available, easy to find and widely distributed.
2) All leaders should have conversations with their teams: what is helpful, what is stressful, what are your signs of stress, how will I know you need help, what are you grateful for, what brings you joy? These are not conversations that you have just once. They are ongoing and help you stay in contact with the level of stress people are experiencing.
3) Health care leaders need to be brave enough to welcome the truth from their people in terms of what their health care providers are feeling and the level of stress. You need to thank people for the information. Information is the only way you will be able to lead effectively and they will only give it to you if you listens and don’t judge or punish.
The Hidden Wound: Moral Injury
But the problem with surviving and healing from trauma is that often the discussion stops with the physiological and psychological impact. The discussion stops at the symptoms of PTSD and never gets to the impact of repeated trauma—the changes we make in ourselves to survive, let alone one of the biggest hidden wounds of trauma: moral injury. We have a self-concept of ourselves as a person with integrity who is helpful and does the right thing. Most people never have to test this self-concept of themselves, and in trauma, this test can be brutal. It can be devastating to a health professional, whose self-concept is to save people’s lives, to watch person after person die, with no real ability to change the outcome. It doesn’t matter if realistically it wouldn’t have been possible there is something mammalian about our desire to be effective in the face of doing our jobs as helpers. Indeed, the search and rescue dogs during 9/11 got so distraught and depressed at not finding survivors that their handlers had first responders hide in the rubble to be found so the dogs didn’t’ experience their own version of moral injury. The psychiatrist Joseph Shay calls PTSD a primary injury--it's symptoms are visible like the break of a bone. But a moral injury is like internal bleeding. It is a silent killer. Soldiers often report feeling like a piece of them died during the war and others have referred to it as ‘soul murder.’
It is important to note that moral injury is not a ‘psychological disorder.’ It’s deeper than that—it hits identity, it hits values, spiritualty, it hits at your very soul. It is the ‘consequence of violating one’s conscience, even if the act was unavoidable or seemed right at the time.[vi]” As health professionals you have a set of beliefs and principles that guide your work and life, “I help save people’s lives” “I never leave a patient to die alone” “I support my coworkers” “I value my family above all” and this crisis doesn’t allow you live those principles at all times and may have you behaving in ways you could have never imagined because it was never required of you. Crucially, it is about you as an individual trying to hold the weight of a collective trauma all by yourself. As a doctor, nurse, respiratory therapist or other health worker helping a patient’s family talk to a dying patient on their Ipad is holding the devastation by yourself, but it shouldn’t be yours to hold alone.
What can Health Professionals Do Right Now:
For war veterans, having to hold their own stories of moral injury—the things that they had to do to survive—is one of the risk factors for suicide with a staggering suicide rate of 22 a day. It is imperative, and may be lifesaving, for you as health professionals to know about moral injury and know that, tragically, it is part of trauma. You will need to need to hold this concept of moral injury for yourself and you need to remind your colleagues. It is a wound that will need healing, but in the short term the most important thing you can do is to not hold your experience and your story alone. This was a world-wide collective trauma. While your individual experiences are personal to you and important to you—the trauma of this pandemic was bigger than you and you must lean on others to hold it. Start with your colleagues and fellow health care workers and share the burdens you are carrying. And then bravely begin to share your stories with your loved ones as you are able, and with the systems and communities within which you work.
What Can Health Care Leaders and Loved Ones Do Right Now:
Health care providers can’t heal without help from loved ones and health care leaders. In order to heal from moral injury health professionals will need to be able to tell their stories, and most importantly, every one of us, from loved ones, to health care leaders to community members are going to have to hold these stories with them. Holding these stories means holding the humanness of not being able to rise to every occasion. It means sitting with the grief and loss and tragedy that this pandemic has wrought. It means not being able to fix it, but instead sit with it. It is, in fact, the opposite of the behavior that we have for Veterans and now for Health Care Workers, where we thank them for the service and call them ‘heroes.’ The problem isn’t that we are grateful and consider them heroic. The problem is that their lived experience of failure and helplessness during their trauma feels so far away from the word ‘hero’ that it makes them feel alien from themselves. And this alienation is dangerous. And most importantly, it keeps them, then, from trying to tell the real story, the real trauma story, where they didn’t feel heroic, or indeed it wasn’t possible to act heroic. In our attempt to be kind, we can cruelly isolate them and that is something we need to avoid. We need to simply listen and acknowledge their sacrifices. We need to let them tell us what it was like. We need for them to not hold it alone.
All of us can make a difference and have an impact on healing. All of us can engage in the small acts of connection. All of us can check in on a colleague or a friend. In fact, in research done by the state of Oregon, the most common response to ‘what does a trauma -informed leader do?” —was ‘they would greet me with a smile. “ We need to remember that no one heals alone. That the antidote to the collective repeated trauma is community.
© 2022 Gretchen L. Schmelzer, PhD
[i] Granek et al., (2012). Nature and Impact of Grief over patient loss on oncologists personal and professional lives. Archives of Internal Medicine 172 964-966. In Ofri, D. (2013). What Doctors Feel. NY: Beacon.
[ii] Gilmartin, K. (2002). Emotional Survival for Law Enforcement: A guide for officers and their families. Tuscon, AZ: E-S Press.
[iii] American Psychiatric Association: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Association, 2013.
[iv] Schmelzer, G. (2018). Journey Through Trauma. NY: Avery.
[v] This citation is a combination of Gilmartin, K. (2002). Emotional Survival for Law Enforcement: A guide for officers and their families. Tuscon, AZ: E-S Press and Siegel, D. (2010). Mindsight. New York, NY: Bantam Books
[vi] Brock, R., & Lettini, G. (2012). Soul Repair: Recovering from Moral Injury after War. Boston: Beacon Press.